Addressing mental health disparities is a critical and complex challenge in psychiatric care, requiring multifaceted approaches to bridge gaps that affect marginalized and underserved populations. Mental health disparities often stem from a combination of systemic inequalities, socio-economic factors, and cultural stigmas, which contribute to unequal access to care and differences in treatment outcomes. These disparities manifest in various forms, including reduced availability of mental health services, insufficient culturally competent care, and barriers related to socioeconomic status, geographic location, and insurance coverage. One key factor in these disparities is the lack of access to mental health services, particularly in rural and underserved urban areas. Individuals in these regions often face shortages of mental health professionals, long wait times for appointments, and limited availability of specialized treatments. This scarcity of resources is exacerbated by geographic isolation, which can make it challenging for individuals to travel to available services.
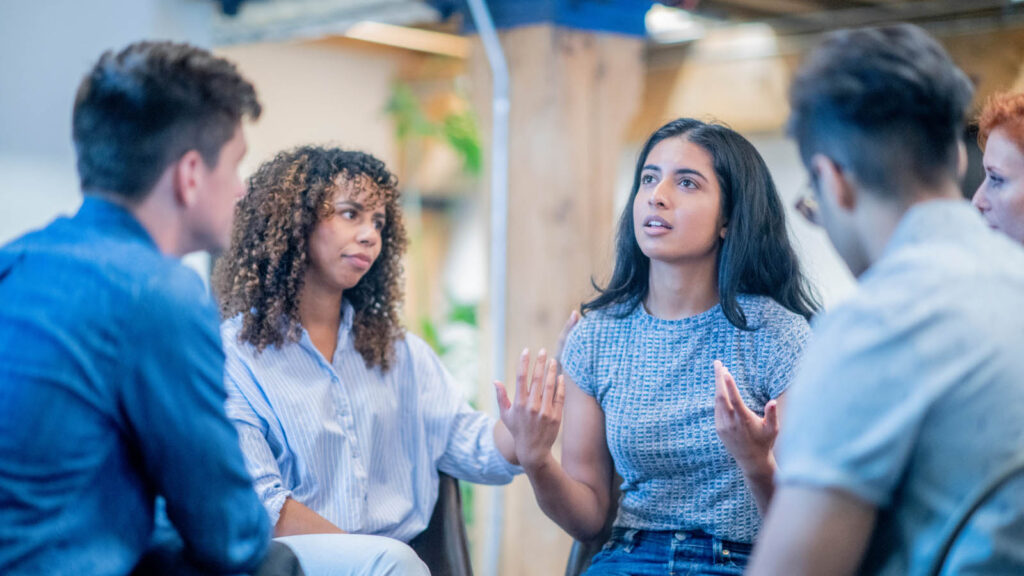 Telehealth has emerged as a promising solution to address these access issues, offering a way to reach patients who might otherwise remain underserved. However, disparities in internet access and technological literacy continue to be barriers to the widespread adoption of telehealth, particularly among lower-income populations. Cultural competence is another crucial aspect of addressing mental health disparities. Many individuals from minority backgrounds face unique cultural and linguistic barriers that can hinder their engagement with mental health services. Providers may lack the training or awareness needed to offer culturally relevant care, leading to misunderstandings and reduced trust between patients and clinicians. Initiatives to improve cultural competence among mental health and wellness professionals, such as training programs and the inclusion of diverse perspectives in clinical practice, are essential for creating an inclusive environment that meets the needs of all patients.
Telehealth has emerged as a promising solution to address these access issues, offering a way to reach patients who might otherwise remain underserved. However, disparities in internet access and technological literacy continue to be barriers to the widespread adoption of telehealth, particularly among lower-income populations. Cultural competence is another crucial aspect of addressing mental health disparities. Many individuals from minority backgrounds face unique cultural and linguistic barriers that can hinder their engagement with mental health services. Providers may lack the training or awareness needed to offer culturally relevant care, leading to misunderstandings and reduced trust between patients and clinicians. Initiatives to improve cultural competence among mental health and wellness professionals, such as training programs and the inclusion of diverse perspectives in clinical practice, are essential for creating an inclusive environment that meets the needs of all patients.
Socioeconomic factors also play a significant role in mental health disparities. Individuals from lower-income backgrounds often experience higher levels of stress and trauma, which can exacerbate mental health issues. Additionally, financial constraints may limit their ability to access care, with many unable to afford out-of-pocket costs or lacking sufficient insurance coverage. Policy changes aimed at increasing funding for mental health services, expanding insurance coverage, and providing financial support for low-income individuals are crucial for mitigating these disparities. Addressing mental health disparities requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach involving policymakers, healthcare providers, community organizations, and the individuals they serve. Efforts must focus on expanding access to care, enhancing cultural competence, and addressing socioeconomic barriers to create a more equitable mental health system. By tackling these issues holistically, we can move toward a future where mental health care is accessible and effective for everyone, regardless of their background or circumstances.
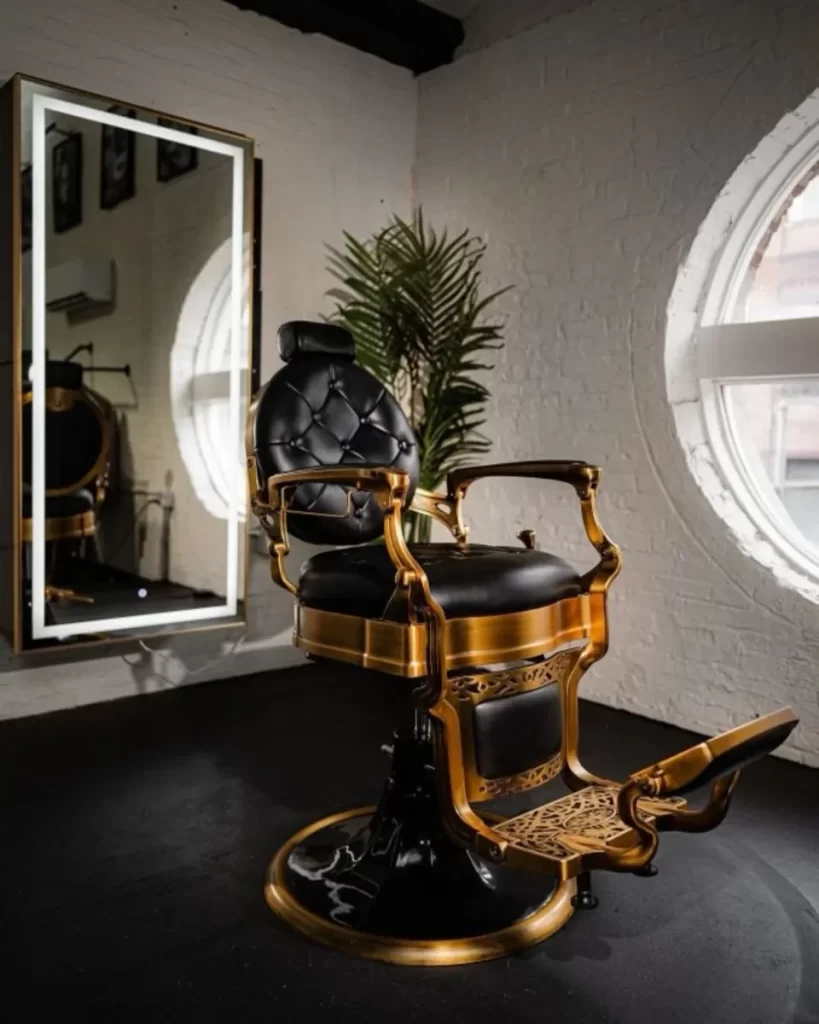





 The design of contemporary barber chairs often incorporates high-quality materials such as premium leather or durable synthetic fabrics that are both aesthetically pleasing and easy to maintain. These materials are chosen not only for their luxury appeal but also for their durability and resistance to wear and tear. The plush cushioning and ergonomic support provided by these materials ensure that clients feel pampered and relaxed throughout their appointment. In addition to comfort and durability, the style of barber chairs has evolved to reflect modern trends. Today’s barber chairs come in various styles, from classic designs that evoke a sense of timeless elegance to sleek, modern looks that add a touch of sophistication to any barbering space. The choice of color and finish can be customized to match the decor of the barbershop, creating a cohesive and visually appealing environment. Ergonomic features extend beyond just comfort and style; they also encompass practical elements that enhance functionality. Many barber chairs are equipped with hydraulic lift systems that allow for smooth and effortless height adjustments.
The design of contemporary barber chairs often incorporates high-quality materials such as premium leather or durable synthetic fabrics that are both aesthetically pleasing and easy to maintain. These materials are chosen not only for their luxury appeal but also for their durability and resistance to wear and tear. The plush cushioning and ergonomic support provided by these materials ensure that clients feel pampered and relaxed throughout their appointment. In addition to comfort and durability, the style of barber chairs has evolved to reflect modern trends. Today’s barber chairs come in various styles, from classic designs that evoke a sense of timeless elegance to sleek, modern looks that add a touch of sophistication to any barbering space. The choice of color and finish can be customized to match the decor of the barbershop, creating a cohesive and visually appealing environment. Ergonomic features extend beyond just comfort and style; they also encompass practical elements that enhance functionality. Many barber chairs are equipped with hydraulic lift systems that allow for smooth and effortless height adjustments.