Heat pumps have emerged as a pivotal technology in the quest for energy efficiency and sustainability, transforming the way we heat and cool our homes. Recent innovations in heat pump technology have significantly enhanced their efficiency, offering substantial reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. At the core of these advancements is the improvement in the heat pump’s coefficient of performance COP, which measures the ratio of heating or cooling provided to the amount of electrical energy consumed. Modern heat pumps can achieve COPs exceeding 4.0, meaning they deliver over four units of heat for every unit of energy consumed. One of the most notable innovations is the development of variable-speed compressors, which allow heat pumps to adjust their output to match the heating or cooling demand more precisely. This flexibility reduces the frequency of on-off cycling, which not only lowers energy consumption but also minimizes wear and tear on the system, leading to longer operational lifespans. Additionally, advanced refrigerants with lower global warming potentials are being utilized to enhance the environmental benefits of heat pumps.
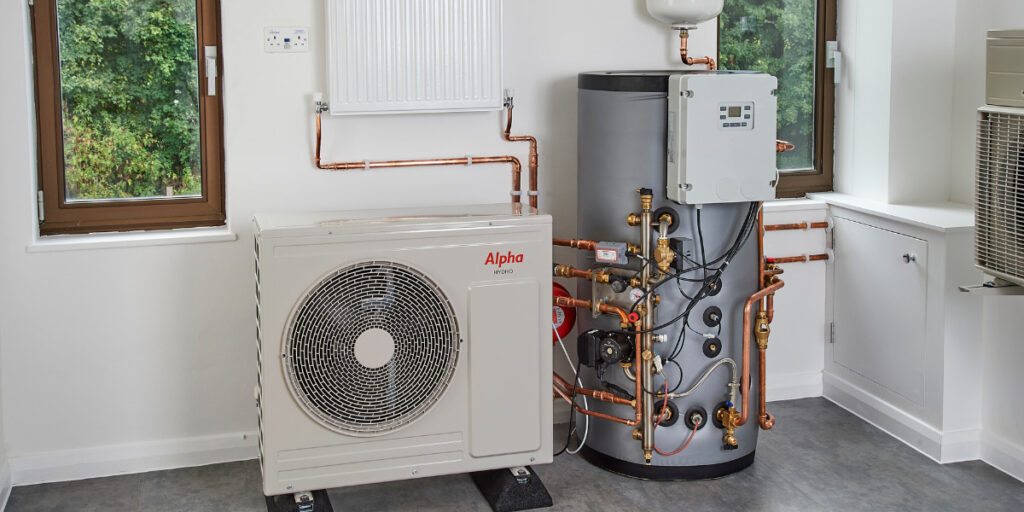

These refrigerants contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining high performance across a range of temperatures. In colder climates, where traditional heat pump efficiency chart might struggle to maintain efficiency, new models incorporating enhanced vapor injection technology are proving effective. These systems are designed to extract heat from the environment even in frigid conditions, thus ensuring consistent performance and comfort. Furthermore, hybrid systems that combine heat pumps with traditional heating sources, such as gas or oil boilers, provide an optimized approach for varying temperature demands, improving overall system efficiency and reliability. The integration of smart technology represents another leap forward in heat pump innovation. Smart thermostats and control systems enable users to program and adjust heating and cooling settings remotely, enhancing energy efficiency by ensuring that the system operates only when needed. Machine learning algorithms within these systems can analyze usage patterns and external weather conditions to optimize performance and energy use further. Another area of innovation is the development of ground-source geothermal heat pumps, which harness the stable temperatures of the earth to provide heating and cooling.
These systems, though initially more expensive to install, offer exceptional long-term energy savings and environmental benefits. Advances in drilling technology and heat exchanger designs are making these systems more accessible and cost-effective, expanding their adoption. The impact of these innovations on energy consumption is profound. By improving efficiency and reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, modern heat pumps contribute to significant decreases in energy bills and carbon footprints. For instance, a well-optimized heat pump system can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 50% compared to traditional systems and view www.jnodenergy.com. As heat pump technology continues to evolve, the potential for even greater efficiencies and environmental benefits is substantial. In summary, the latest innovations in heat pump technology are transforming the landscape of energy consumption. Through advancements in compressor technology, refrigerants, smart controls, and ground-source systems, heat pumps are becoming more efficient and environmentally friendly. These improvements not only offer substantial cost savings but also play a crucial role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing our environmental impact.